Hermetically sealed pumps for extreme liquids are the core competence of HERMETIC-Pumpen
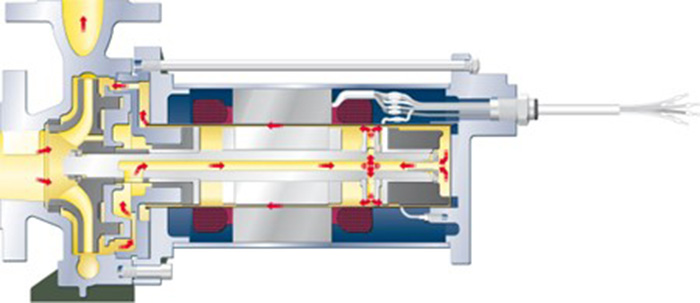
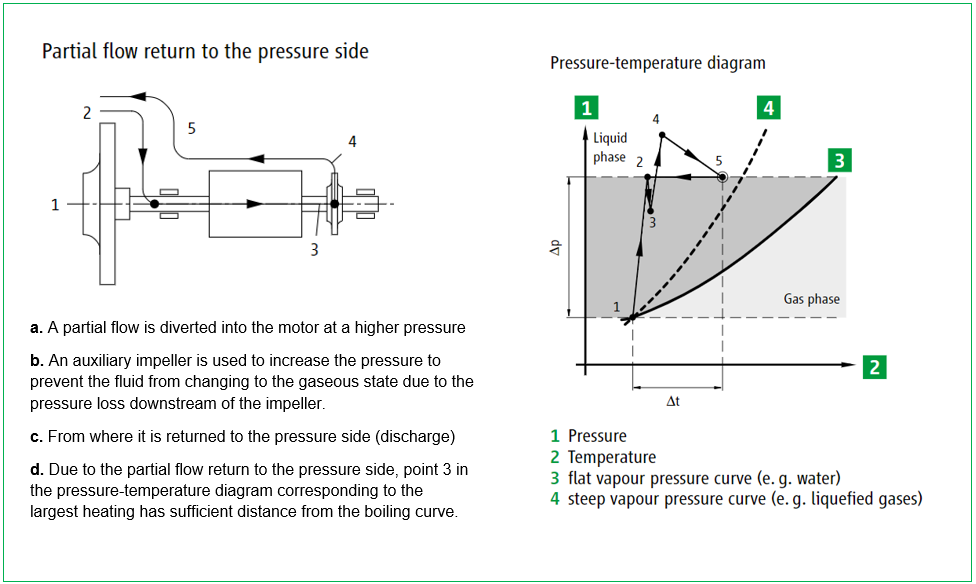
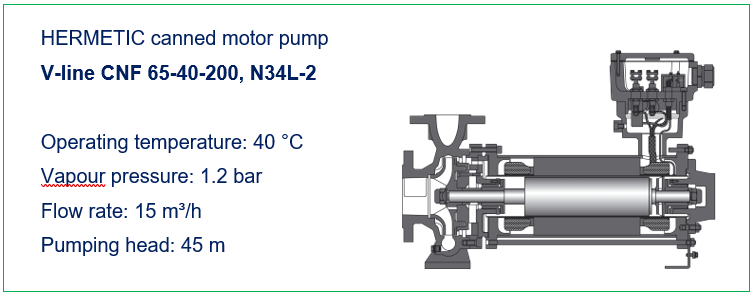
Hermetically sealed, low-maintenance pumps that are suitable for extreme application areas and hazardous pumped liquids are the core competency of HERMETIC-Pumpen GmbH. With its CAMT and CNF series, the canned motor pump specialist provides safe and durable units that offer system operators a number of advantages for the production process of ammonia when compared to conventional centrifugal pumps. While the CNF series with an integrated auxiliary impeller and internal fluid return system is specifically designed for pumping liquefied gases as well as boiling media and condensates, the tandem configuration of the CAMT series offers an effective solution for pumping small quantities at high pumping heads, as is typically the case when pumping liquid ammonia into a storage tank.
Ammonia, the chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, with the formula NH3, is, with an estimated 180 million tons a year, one of the most frequently produced chemicals worldwide (figure from 2021). Roughly 75 per cent are being used for the production of fertilisers. Various substances derived from ammonia serve as starting materials for polymers. As a fire-resistant, non-hazardous refrigerant with regard to the greenhouse effect, ammonia is being used in refrigeration technology. In the quest for alternative fuels, ammonia is also increasingly brought up as a topic for discussion as a potential hydrogen carrier as well as an alternative to hydrogen.
Production of ammonia
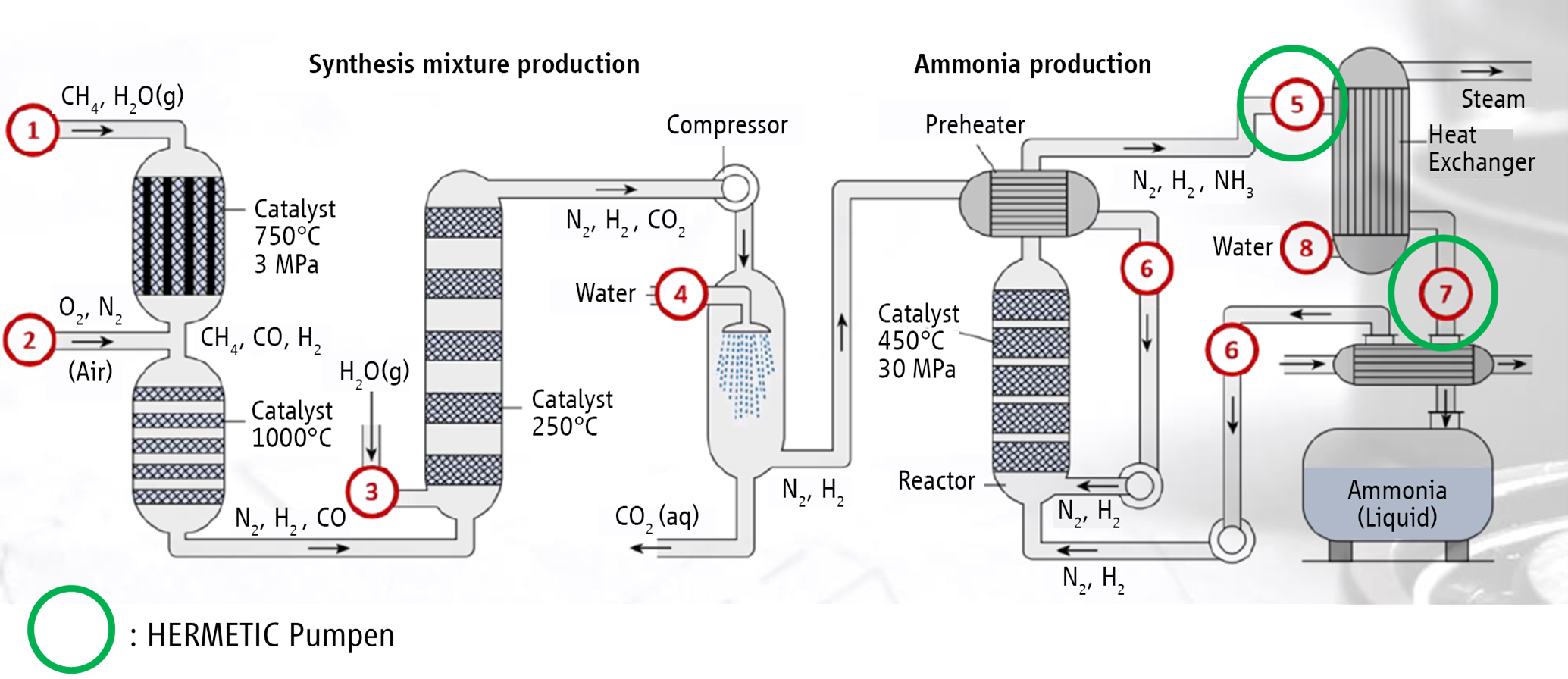
Ammonia is produced from hydrogen and nitrogen. A synthesis process according to the Haber-Bosch method is applied most commonly. In recent years, however, research has increasingly focused on alternative processes since high carbon dioxide emissions and a high energy consumption are associated with the Haber-Bosch method. The starting materials for ammonia synthesis are gained by way of a process known as steam reformation. The resulting synthesis gas mainly consists of hydrogen and nitrogen.
Ammonia synthesis
In order to synthesise ammonia, a turbo compressor is used to compress the synthesis mixture to 250 to 300 bar, so that the actual ammonia synthesis can take place in the reactor at 400 to 500 °C.
The reactor catalyst is made of specially prepared iron, which contains traces of potassium, aluminium, calcium, magnesium and oxygen. This is where the diatomic oxygen molecules and hydrogen molecules split and chemically bond with an atom of the other element to form ammonia. Ammonia can then be continuously removed from the process, and continually cooled in a heat exchanger with water, supplied gases and/or other process flows. Due to being cooled down, the ammonia condenses and can be removed from the cycle by means of a high-pressure separator. The non-reactive oxygen components and hydrogen components are brought back to operating pressure and added to the synthesis gas. Sometimes the produced ammonia is distilled to increase its purity. The ammonia is then cooled so that it becomes a liquid that can be stored in large tanks.