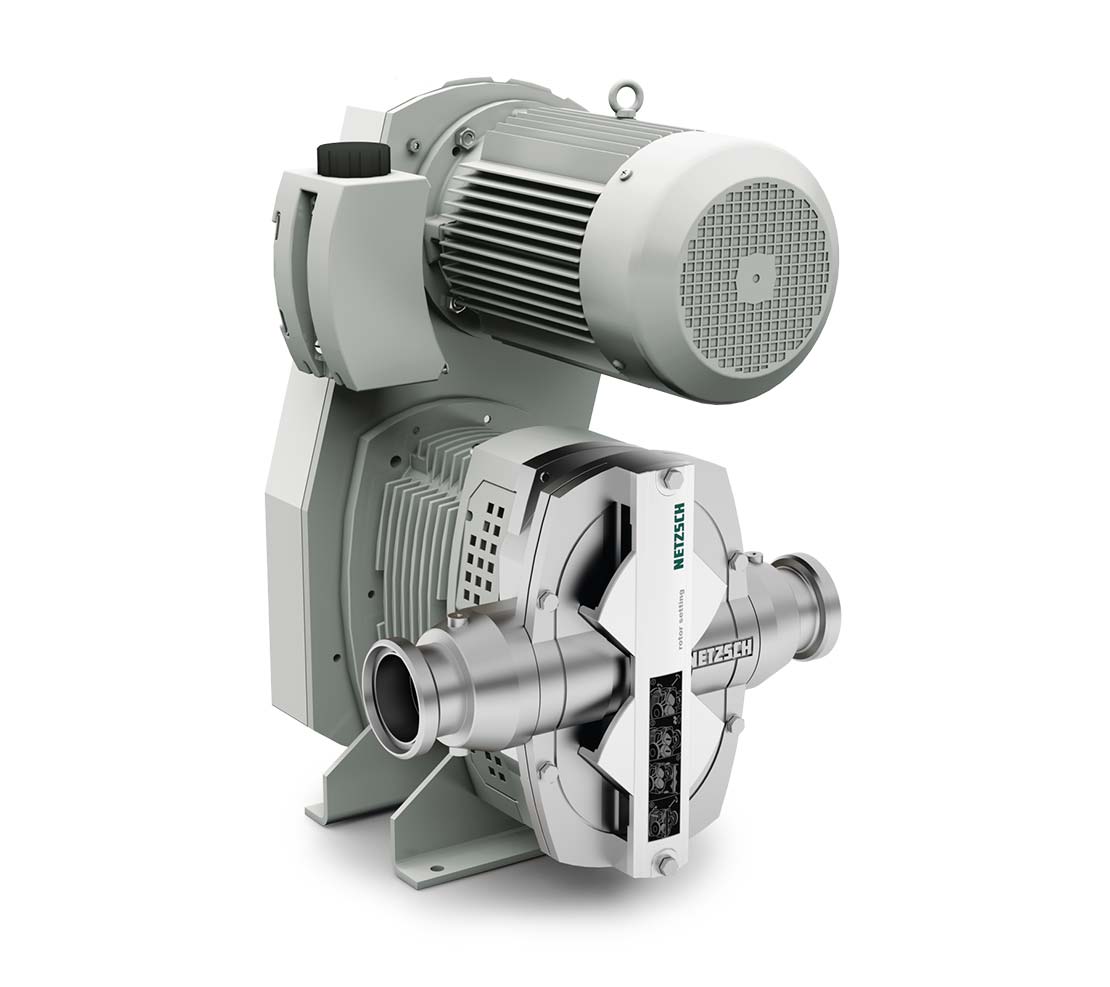
Outstanding performance with compact design and easy service: Among the various types of positive displacement pumps, rotary lobe pumps, or also calles rotary piston pumps, win people over with their elegant simplicity. Two pistons with one to three blades and a reliable drive – nothing more is needed to achieve high efficiency and a long service life. That’s how these pumps offer outstanding performance with easy service.
Rotary Lobe Pumps
Technical Data & Characteristics:
- Delivery rate: up to 1,000 m³/h (4403 gpm)
- Delivery head: up to 180 m (590 ft)
- Pressure: up to 18 bar (261 psi)
- Viscosities: up to 100,000,000 cSt
- Temperature: up to 200 °C (392 °F)
- pH-value: 1 – 14
- Gases: up to 95 %
- Solids: up to 60 % (max. 70 mm)
- Installations: horizontal, vertical
- Submersibilities: immersed, submerged
- Depth: up to 10 m (33 ft)
- self-priming possible
- ATEX: suitable for ExZones 1 & 2
- API, ISO, EN standard
- hygienic design available
- Drives: electro, diesel, hydraulic
The operating principle of a rotary lobe pump is nearly self-explanatory: Two pistons that dovetail with one another rotate in the casing. The pistons can also have two or more blades. Due to the rotation of the rotor pair, negative pressure is created on the suction side, which takes in the liquid and conveys it along the pump wall to the pressure side.
Rotary piston pumps with rubberized rotors close up almost completely when they are shut down. If the rotary pistons are made of metal, the necessary undersize prevents a complete seal. These are opposed to some types of rotary lobe pumps with rubberized flanks on the pistons that ensure sealing.

Like other technologies among the positive displacement pumps, rotary lobe pumps can be used in a broad spectrum of applications. These flexible multi-talents have some advantageous properties. They are:
- self-priming
- valve-less
- compact
- powerful
- safe
Thanks to their simple design, rotary piston pumps can handle both low and high-viscosity media. Due to their large free ball passage and low speeds, they are not sensitive to clogs, build-up or foreign bodies. Different solid contents influence the pump output just as little as pressure changes caused by the solid quantity.
In contrast to rotating transporting units such as centrifugal pumps, there are no large centrifugal or shear forces that affect the fluid when conveying liquids.
Therefore, these modest pumps are also suitable for transporting shear-sensitive media. For the same reasons, even abrasive liquids can do relatively little to the casing and the pumps’ rotary pistons. Due to their displacing conveying principle, they can handle non-lubricating and lubricating media safely.
Rotary piston pumps have a higher efficiency than that of some other displacement pumps. Since the energy costs make up the largest share of the life-cycle costs of a pump, the high efficiency provides cost advantages that extend across the entire life cycle of the pump.
Easy maintenance without special tools
The simple design also has a positive effect on operation: If a rotary piston has to be exchanged due to wear, leading manufacturers’ pumps enable quick replacement without special tools and in a very short time. In some cases, it is even possible to remove the casing cover and pistons with knurled-head screws without any tools at all. Operators also save money when no specially trained personnel is required for servicing and maintenance.
Their flexibility makes rotary lobe pumps suitable for use in many industries and for handling various liquids. Especially their tolerance for media containing solids combined with their large ball passage mean that powerful displacement pumps are used to handle heterogeneous fluids: as slurry pumps, wastewater pumps or to drain containers. For drainage, the additional benefit of easy reversing of the flow rate is brought to bear: Reversing the direction in which the piston is rotating is enough to reverse the handling direction.
Since rotary piston pumps can handle both low- and high-viscosity media, they are popular in the food industry, since there the viscosity of liquids to be handled changes frequently; for example with molasses or magma (a mixture of crystallized sugar and concentrated juice) in sugar manufacturing. That’s why rotary piston pumps with hygienic designs are often used in the food and pharmaceutical industries when required.
The material for rotary piston pump components can be selected according to the application: Typically, the pistons are rubberized; the parts of the casing in contact with media are made of metal. This way, when the pump is shut off, there is a nearly complete seal.
For particular applications, however, there are also rotary piston pumps where both the inside of the casing and the pistons are made of metal (steel or stainless steel). In this case, the pump is constructed with undersize in order to prevent damage. Rotary piston pumps designed this way are especially robust and resistant to abrasion. However, there is no complete seal.
Rotary piston pumps that are designed to be especially robust and have a long service life with low maintenance effort are a special case. Here, the material selection is the other way around: Instead of rubberized pistons in a metal casing, hardened steel pistons rotate in a simple rubber casing insert that can be replaced easily.
Since steel is less subject to material fatigue due to dynamic forces, this ensures that the rotors will last longer. Furthermore, the metal deforms less under changing temperatures. This way, the rotary pistons can be manufactured with tight tolerances, which makes them efficient and enables them to run at low speed. In turn, this means that components are spared, and wear is reduced, so that service life can be increased.
Their self-priming handling; resistance to abrasive, high-viscosity liquids or those containing solids and easy maintenance enable rotary lobe pumps to be deployed easily in harsh environments where things can get rough sometimes.
Users can take advantage of the numerous benefits of the handling principle with two- or three-bladed lobes even in sensitive areas such as the food and pharmaceutical industries, for these pumps are also available in hygienic designs. They are typically all metal and have a series of hygiene certificates from EHEDG about the 3A Sanitary Standard for the specifications of the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA).


